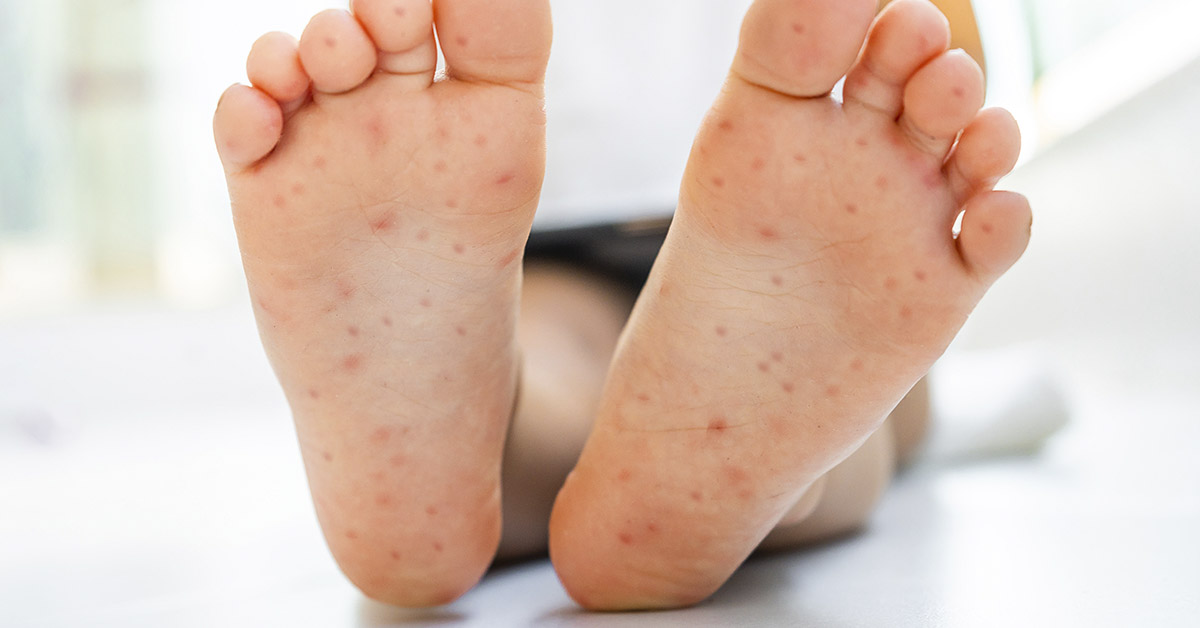
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) is a viral infection that commonly affects young children. Caused by the coxsackievirus or enterovirus, it presents symptoms such as blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth. It spreads through physical contact or exposure to contaminated surfaces.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
If your child exhibits a high fever, sore throat, general malaise, mouth sores, rash, fussiness, and loss of appetite, they may have contracted HFMD. It’s important to look out for and recognize these symptoms.
Prevention and Precautionary Measures
Encourage proper hygiene, such as frequent hand washing, covering the mouth when sneezing or coughing, and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces. Avoid close contact with infected individuals and do not share personal items to prevent transmission.
What to Do if You Suspect Your Child Has HFMD
If you think your child has HFMD, consult a healthcare professional, practice self-isolation, provide proper care, manage fever and discomfort, and maintain good hygiene to prevent the spread of the virus.
While HFMD is not overly dangerous, it is uncomfortable. Teaching your children proper hygiene can help prevent it. Always consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Sources
- “Hand-foot-and-mouth disease.” Mayo Clinic
- “Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease.” Kids Health





