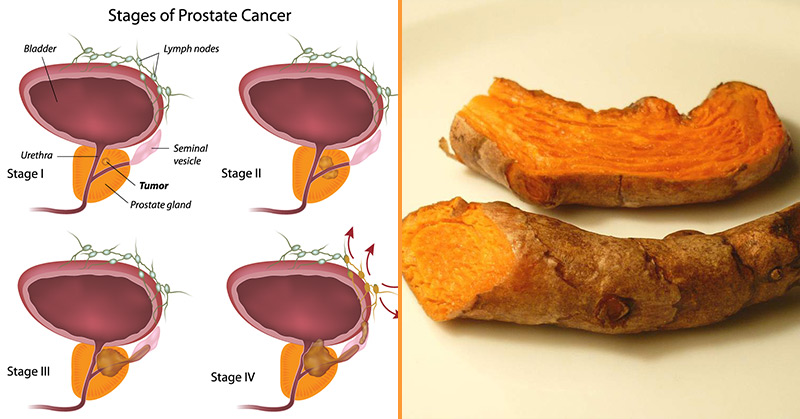
Over the past three decades, there has been a decline in the incidence of prostate cancer since its peak in the mid-1990s. However, prostate cancer remains the most common cancer among American men after skin cancer. The American Cancer Society predicts that doctors will diagnose another 299,010 individuals with prostate cancer in 2024, with 35,250 expected to die from it.
Aside from prostate cancer, many men also face issues with their prostates, such as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), also known as prostate enlargement. BPH occurs when the prostate gland becomes enlarged, a condition that affects men at different stages in life. Factors that increase the likelihood of developing BPH include being at least 40 years old, being obese, and having a history of heart or circulatory disease, type 2 diabetes, physical inactivity, or erectile dysfunction.
While both prostate enlargement and prostate cancer affect the same gland, they are distinct conditions. BPH is non-cancerous and cannot spread elsewhere in the body, whereas prostate cancer is malignant and requires specific treatment. Symptoms that may overlap between the two conditions include urgent or excessive urination, difficulty urinating, and weak urine flow.
To maintain a healthy prostate and reduce the risk of prostate cancer, there are dietary and lifestyle changes that men can make. Certain foods have been associated with either increasing or decreasing the risk of prostate cancer. Foods to include in your diet for a healthy prostate include organic fermented soy products, omega-3 fatty acids, flaxseed, vitamin E, selenium, lycopene, vitamin D, berries, and green tea.
Incorporating these foods into your regular meals can help promote a healthy prostate and lower the risk of prostate cancer. Research has shown that specific nutrients present in these foods have protective effects against prostate cancer. It is essential to make informed choices about your diet to reduce the risk of developing prostate-related health issues.