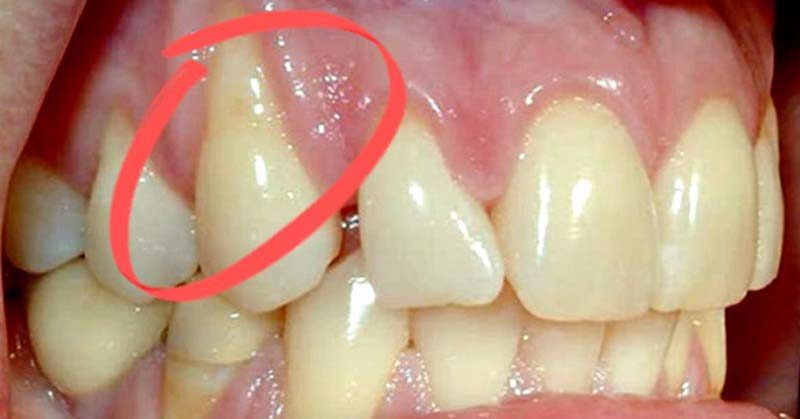
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common dental issue affecting millions of adults in the United States. According to the CDC, over 47% of adults over the age of thirty have some form of periodontal disease, with those over 65 having an even higher prevalence [1]. This condition not only affects oral health but has also been linked to other serious health problems, including cancer.

What Causes Gum Disease?
Gum disease is primarily caused by the build-up of plaque around the teeth, leading to bacterial infections and inflammation in the gums [2]. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a severe condition that can result in tooth loss.
Gum Disease and Cancer
Recent studies have shown a correlation between gum disease and cancer, with the bacterium Treponema denticola (Td) implicated in the development of certain types of cancers [3]. Researchers have found that Td and some gastrointestinal cancers share specific enzymes that promote cancer cell growth.
The link between periodontitis and cancer mortality was further supported by a large-scale study, indicating a higher risk of cancer-related deaths in patients with periodontal diseases [5]. This suggests that treating and preventing gum disease could potentially reduce the risk of developing and succumbing to cancer.
Oral Health and Disease
Gum disease not only poses a threat to oral health but is also linked to various other health conditions, including endocarditis, cardiovascular disease, pregnancy complications, pneumonia, and more [6]. Additionally, certain health conditions like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, osteoporosis, and Alzheimer’s disease can contribute to the development of gum disease.
How to Protect Your Oral Health
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, is essential for preventing gum disease and its associated health risks [2]. The American Dental Association recommends specific guidelines for proper dental care to reduce the risk of gum disease.
In cases of advanced periodontitis, additional treatments like medication or surgery may be necessary. Prescription mouthwashes and oral antibiotics can help control the progression of gum disease and prevent further complications.
Overall, prioritizing oral health through a consistent hygiene routine can not only prevent gum disease but also lower the risk of developing serious health conditions like cancer. Taking care of your oral health is an important step towards maintaining overall well-being.