Early detection is crucial in determining the success of cancer treatment, particularly in cases of lung cancer, which is a common and deadly form of cancer. The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) developed the TNM Staging System to classify cancer cells and determine the extent of the disease. This system helps oncologists design appropriate treatment plans to achieve progression-free survival. Lung cancer is classified into different types based on histology, with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) being the most common.
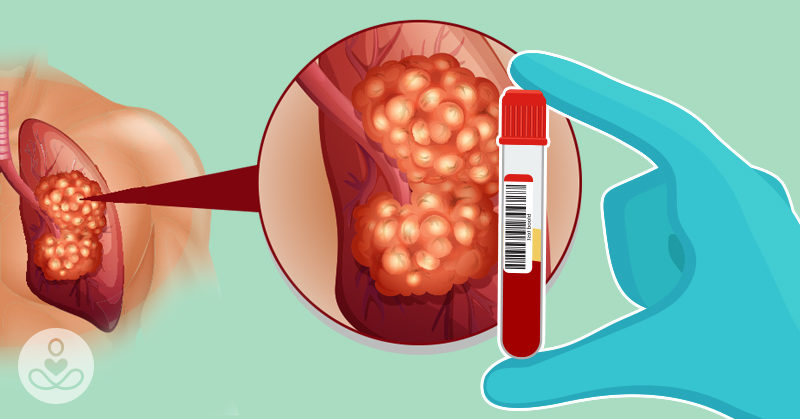
Traditional methods of lung cancer screening involve imaging technology and tissue biopsies, but these methods are often only used when there is a suspicion of cancer. A new approach using molecular diagnostics, such as liquid biopsy, has shown promising results in early detection of lung cancer. This non-invasive method involves analyzing blood plasma for cancer-related biomarkers, including mutated circulating tumor DNA. This approach has been approved by the FDA for identifying patients with metastatic NSCLC and may soon replace traditional screening methods like CT scans.
The development of molecular technology, such as liquid biopsy, has the potential to revolutionize cancer detection and treatment. GRAIL, Inc. is leading a global initiative to develop early cancer detection methods using genomic molecular testing technology. Their ongoing CCGA study has shown promising results in detecting early-stage lung cancer through blood testing. This technology holds the promise of detecting cancer cells before tumors form or symptoms appear, potentially saving countless lives. Further research is needed to confirm the efficacy of liquid biopsy tests in detecting recurrence and disease progression in lung cancer patients.