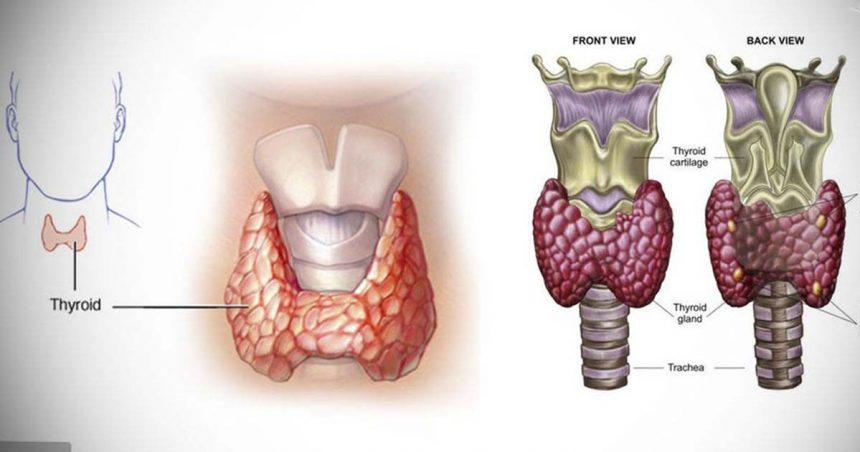
The thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland in your neck, produces hormones like thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin regulating crucial body functions. With an estimated 20 million Americans affected by thyroid disorders, 60% are unaware of their condition, highlighting the need for awareness (1).
Understanding Your Thyroid and Its Functions
Controlled by the pituitary gland, the thyroid plays a vital role in metabolism, growth, and body temperature regulation. Dysfunction in either gland can impact overall health, showcasing symptoms of thyroid disorders like hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and goiter with varying severity consequences if left untreated (1).
Identifying Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, characterized by excessive hormone production, leads to symptoms such as nervousness, weight loss, rapid heartbeat, muscle weakness, and more physical signs like goiter, palpitations, and sweating, requiring prompt medical attention (2).
Recognizing Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, marked by insufficient hormone production, presents symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, and other health issues, often stemming from immune disorders like Hashimoto’s disease or certain medications (3).
Steps to Take If Suspecting Thyroid Disease
If experiencing any mentioned symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and appropriate testing. Treatment may involve hormone replacement therapy for hypothyroidism or medications to regulate hormone levels for hyperthyroidism to ensure optimal thyroid function.
For more information, continue reading: 8 Medications That May Cause Hypothyroidism
Sources
- “Prevalence and Impact of Thyroid Disease.” Thyroid
- “Symptoms-Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)” NHS
- “Causes– Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)” NHS